Introduction to Smart Contracts
What Are Smart Contracts?
Definition and Origin
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with the terms directly written into code. Introduced in the 1990s by Nick Szabo, they eliminate intermediaries by using blockchain technology to enforce and execute agreements automatically.
How They Differ from Traditional Contracts
Unlike traditional contracts, which require legal teams and third-party oversight, smart contracts operate autonomously. Their execution depends solely on the predefined code and conditions.
The Role of Blockchain Technology in Smart Contracts
Blockchain serves as the backbone of smart contracts, providing a decentralized, tamper-proof environment. This ensures transparency and immutability, making smart contracts a reliable alternative to traditional agreements.
How Smart Contracts Work
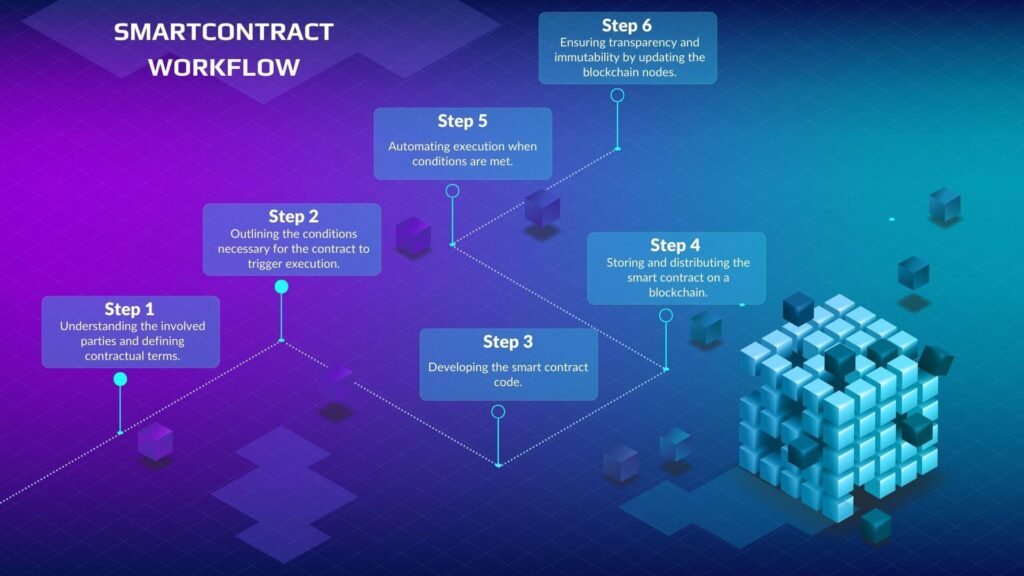
Key Components of Smart Contracts
Code
The logic and conditions of a smart contract are programmed into a code, which acts as the legal language of the agreement.
Blockchain Platform
Smart contracts are deployed on blockchain platforms, where they are immutable and publicly accessible.
Execution Process
Deployment on the Blockchain
Once coded, smart contracts are deployed on a blockchain platform, where they become part of the distributed ledger.
Automatic Triggering of Conditions
When the specified conditions are met, the smart contract executes automatically, ensuring timely and precise fulfillment of agreements.
Security and Transparency
The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that smart contracts are tamper-proof. Transparency is enhanced as every transaction is recorded on the blockchain.
Advantages of Smart Contracts
Automation and Efficiency
Smart contracts eliminate the need for manual intervention, speeding up processes and reducing errors.
Cost Reduction
By removing intermediaries, businesses save on administrative and legal fees.
Trust and Transparency
Every participant can view the contract’s execution, fostering trust and eliminating the potential for disputes.
Decentralization
Smart contracts operate independently of centralized authorities, ensuring impartiality and security.
Limitations and Challenges
Scalability Issues
Blockchain networks face scalability challenges that can slow down contract execution during high traffic.
Legal and Regulatory Challenges
The legal status of smart contracts is still evolving, with many jurisdictions lacking clear regulations.
Programming Bugs and Security Risks
Errors in coding can lead to vulnerabilities, making it essential to thoroughly audit smart contracts.
Real-World Applications of Smart Contracts
Finance and Banking
Automated Payments and Settlements
Smart contracts facilitate instant payments, reducing settlement times and associated costs.
Insurance Claims Processing
By automating claims approval, smart contracts streamline the insurance process.
Supply Chain Management
From tracking shipments to automating payments, smart contracts bring transparency and efficiency to supply chains.
Real Estate
Automated Property Transfers
Ownership transfers are streamlined with smart contracts, eliminating the need for lengthy paperwork.
Escrow Services
Smart contracts act as digital escrow agents, ensuring secure and efficient transactions.
Healthcare
Smart contracts improve patient data management and automate billing processes.
Gaming and Entertainment
From in-game asset ownership to royalty payments, smart contracts revolutionize the digital entertainment space.
Popular Platforms for Smart Contracts
Ethereum
The pioneer in smart contract platforms, Ethereum offers robust functionality and widespread adoption.
Binance Smart Chain
Known for lower fees and high-speed transactions, Binance Smart Chain is a popular choice for developers.
Solana
With its high throughput, Solana is ideal for applications requiring fast execution.
Polkadot
Polkadot enables interoperability between blockchains, enhancing smart contract versatility.
The Future of Smart Contracts
Integration with AI
Combining AI and smart contracts can enhance decision-making and create adaptive agreements.
Mass Adoption Across Industries
As technology evolves, smart contracts are poised to disrupt numerous industries, from healthcare to finance.
Conclusion
Smart contracts are transforming the way agreements are made and executed. With their automation, transparency, and efficiency, they offer unparalleled advantages across various industries. While challenges remain, the potential of smart contracts to revolutionize how we interact and transact is undeniable
FAQs
- What makes smart contracts secure?
Their immutability and execution on blockchain make smart contracts tamper-proof. - Are smart contracts legally binding?
In many jurisdictions, they are recognized as enforceable agreements, though legal clarity varies. - Can smart contracts operate without blockchain?
No, blockchain is integral to their decentralized and secure functionality. - What industries benefit most from smart contracts?
Finance, real estate, supply chain, and healthcare are among the top beneficiaries. - How do smart contracts affect traditional jobs?
They reduce reliance on intermediaries, leading to job transformation rather than elimination.